Why is a Password Manager so Critical?
The average person has 70 to 80 passwords connected to business and personal accounts. If you’re chronically online like the rest of us, that could easily look like 300+ passwords. Passwords are one of the first layers of account protection and act as a vital defense mechanism, protecting our sensitive information, personal data, and online accounts from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
When it comes to cybersecurity, managing the password jungle is one of the biggest challenges for individual users and companies. If your company still needs a password management system, your employees and clients are at a higher risk of being compromised.
So how can you patch this potential hole? By setting up a password manager company-wide.
What is a Password Manager, and Why is it Useful?
A password manager is a software tool or application designed to securely generate, store, and manage a user’s logins and passwords.
It’s challenging to create unique and complex passwords for each account, let alone keep track of them all. Microsoft found that 73% of users duplicate their passwords in both their personal and work accounts. Investing in a password manager for your team can alleviate the burden of generating, securely storing, and remembering multiple complex passwords for different accounts, which adds another layer of security to your organization.
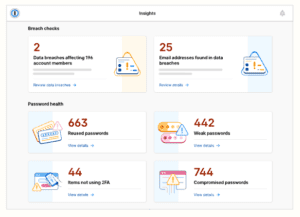
Most password managers have the following features:
- Master Password. A master password is what safeguards access to the rest of your account. This master password should be unique, long, complex, and memorized by you.
- Password generation. When creating a new account, auto-filled strong password suggestions help make the process easier.
- Secure storage for your passwords. The software ensures they are encrypted and protected from unauthorized access.
- Manage your passwords. Some password managers have alerts for when you’ve reused a password, a password was discovered in a breach, 2FA is available (and not currently set up) for a particular site, and more.
- Secure sharing. If you need to share login credentials, many password managers allow you to create shared vaults for people that share login details.
- Additional storage for sensitive information. Credit card details, secure notes, documents, bank accounts, IDs, and more are all securely stored in one place.
Three Steps to Secure Your Company’s Passwords
Step One: Choose a Password Manager
First, you need to pick a password manager for your company. But there are some important things to consider like:
- User Management Tools: Evaluate the user management capabilities of the password manager. Will it let you easily manage user access and password sharing? Can it handle multiple users or teams within your organization?
- Compliance Requirements: Depending on your industry, you may have specific compliance requirements, such as password health monitoring or the ability to generate compliance reports. Ensure that the password manager you choose provides the necessary security measures to safeguard sensitive information.
- Usability and User Experience: Consider the ease of use for your team members. A password manager that is intuitive and user-friendly will help encourage use and minimize the learning curve. To enhance usability, look for features like browser extensions, autofill capabilities, and synchronization across devices.
Popular Password Manager Options (+ What We Recommend!)
So, what are some of the most popular password managers that are worth investing in?
- 1Password: A popular choice offering a comprehensive suite of features, including secure password storage, document storage, and sharing capabilities. It integrates well with various platforms and provides advanced security options like two-factor authentication.
-
- At Edge Networks, our personal choice and recommendation is 1Password. Its user-friendly interface, comprehensive features, and reputation as one of the most secure password vaults make password management as easy as possible.
- LastPass: A widely recognized password manager known for its robust security features, intuitive interface, and multi-platform support. It offers both personal and business plans, allowing you to scale as your company grows.
- Dashlane: It offers an intuitive and user-friendly interface, making it easy for teams to adopt. It provides features like password autofill, password generation, and secure note storage. Dashlane also offers business plans tailored to meet the needs of organizations.
- Keeper: Known for its security features, including strong encryption and zero-knowledge architecture. It offers a range of features like password sharing, role-based access control, and compliance with various industry regulations.
Why We Don’t Recommend Google Password Manager
There are many password manager options out there, and it can be hard to decide which one to invest in. Many people go for what’s most convenient and free, such as Google Password Manager. If that sounds like you, we have some news for you: While Google Password Manager may seem convenient for managing passwords, there are several reasons why it may be advisable to avoid relying solely on it and opt for dedicated password managers instead:
- Dependency on Google Account: Google Password Manager is directly tied to your Google account. Someone who gains unauthorized access to your Google account can access all your stored passwords. This concentration of sensitive information within a single account poses a higher risk than dedicated password managers, which often employ additional security measures to protect user data.
- Less Focus on Security: While Google takes security seriously, dedicated password managers typically prioritize security as their primary focus. They employ robust encryption algorithms, zero-knowledge architectures, and other security measures to protect stored passwords. Dedicated password managers are often independently audited for security and undergo regular security updates, enhancing their ability to protect passwords.
- Limited Features: Google Password Manager offers basic password storage and autofill capabilities but lacks many advanced features in dedicated password managers. Features like password sharing, secure note storage, and password auditing are often absent in Google Password Manager, limiting the control and functionality available to users.
Step Two: Setting Up the Password Manager
Once you’ve chosen your password manager, it’s time to set it up. The size of your organization and how many passwords each user has will determine how long this step takes.
- Create a Master Account: Establish a central master account within the password manager. This account will serve as the mothership for your cybersecurity team, allowing them to manage user accounts, access permissions, and other administrative tasks. Setting up the master account typically involves a strong and unique password, as it holds the key to your organization’s password management system.
- Configure Settings: Customize the password manager’s settings to align with your organization’s security policies and requirements. This includes defining password requirements like complexity rules, minimum length, use of special characters, restrictions on password reuse, and other relevant criteria. Enable features like two-factor authentication (2FA) to add an extra layer of protection to your password manager. Be sure to fine-tune the settings based on your organization’s specific needs.
- Import Existing Passwords: Most password managers can import passwords from various sources, simplifying the transition process. You can import passwords from web browsers, CSV files, or other password managers. This enables smooth migration of existing passwords into the new password manager, minimizing the burden on users to manually re-enter their credentials. However, if passwords are stored in handwritten or non-digital formats, adding them to the password manager may require manual input, which can be time-consuming.

Step Three: Train Your Team
Now that you have successfully set up your password manager, you must provide comprehensive training to your team members on how to use this valuable tool. It is important to consider different learning styles and ensure the training materials are accessible to everyone.
We suggest creating a detailed, text-based Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) that outlines the step-by-step process of using the password manager. This text-based guide should include clear instructions accompanied by screenshots or visual aids to help users understand each stage of the process. This also allows your team to refer to the SOP whenever needed and follow the instructions at their own pace.
You can complement the text-based SOP by creating a video guide visually demonstrating the same procedures. This video can be recorded using screen capture software, displaying the password manager’s features and functionalities in action. A video guide is especially beneficial for individuals who prefer visual and auditory learning, as they can watch and listen to the instructions in real time.
Training is an ongoing process, especially as new team members join or the password manager evolves. Regularly communicate with your team, gather feedback, and promptly address any issues or concerns. Investing time and effort into training and learning resources enables your team to confidently utilize the password manager’s features, ensuring consistent and secure password management practices across your organization.
Setting Up Your Password Manager Doesn’t Have to Be a Burden
If the idea of overhauling your company’s password management system seems overwhelming, rest assured – you’re not alone. We recognize that cybersecurity can be time-consuming and are here to alleviate that burden for you. At Edge, we’re all about helping you reach your security goals while providing clarity for you every step of the way.
Contact us today if you are looking to improve your organization’s cybersecurity without sacrificing your precious time and resources. We would love to help you.