The Human Element in Cybersecurity
When it comes to cybersecurity, we often focus on things like firewalls and antivirus software as our primary defense. However, at its core, cybersecurity is heavily influenced by something even more critical – humans.
Let’s start with a definition of cybersecurity: “Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and digital data from unauthorized access, breaches, damage, or theft while ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.”
So, how does the human element tie in? Well, as it turns out, humans have everything to do with cybersecurity.
You may have heard of the recent MGM attacks, where the casino industry confronted a wave of cyber-attacks orchestrated by the advanced “Scattered Spider” group. Caesars Entertainment fell victim to the attack, with a breach targeting its loyalty program, potentially compromising customer data.
The incident began with a social engineering breach, exploiting vulnerabilities at the IT help desk. This paved the way for a complex intrusion, shaking the foundations of MGM Resorts’ cybersecurity infrastructure.
As we can see, the best tools on the market aren’t foolproof if the humans they’re protecting aren’t educated and motivated to defend against cybersecurity attacks. I’d be willing to bet they’ll implement mandatory security awareness training on social engineering and hardening their employee identification and authentication procedures going forward.
My Experience at the Oregon Cyber Resilience Summit 2023
The concept of the human element in cyber defense was highlighted often at the Oregon Cyber Resilience Summit, which I recently had the pleasure of attending. The theme of the event was “Building a Secure Community,” and I was shocked that each and every speaker had a tie back to building a strong cybersecurity culture and how absolutely critical it is to focus on human-centric attacks.
Matt Singleton at CrowdStrike highlighted excellent key points, including the importance of putting a profile of the likely threat actors your company may encounter based on industry, size, and location. Other key points included the criticality of evolving our response speed and defenses to the new challenges of the cloud, banding together as a community to protect ourselves against adversaries that are teaming up, mitigating against exploitable human errors to the best of our ability, and applying timely security patches to take full advantage of the defensive resources available to all of us.
A wonderful Palo Alto representative had new insights in our discussion of the challenge to empower our organizations and cybersecurity teams with appropriate playbooks. This highlighted the common struggle to ensure our teams are equipped and prepared with defined steps to follow for a strong cybersecurity culture full of repeatable, well-known procedures to follow and the importance of communicating that information to the relevant stakeholders.

Ted Fitzgerald of Curry County had all of us in stitches listening to his Lessons Learned from their recent ransomware attack. He practiced what he preached in demonstrating to us the importance of sharing cyberattack experiences to build community awareness and a collaborative cybersecurity culture in which we can share information, lessons learned, support, and maybe even laughs as we navigate stressful and often puzzling cyberattacks.
What really hit me was a talk from Ryan Kalember at ProofPoint, a leading cybersecurity vendor, which I’ve mostly experienced through the email security lens. Ryan spoke about the increasing trend of humans targeting humans, Business Email Compromises (BECs), supplier compromises, and other trending human-centric attacks. This really made me think about the root cause of each of these trends… potentially, a lack of an adequately strong culture in which cybersecurity is emphasized and prioritized. Your best defense against your people being targeted through social engineering is to educate them on all of the different common social engineering tactics and vectors.
The Human Element: Social Engineering and What to Look Out For
I’ve presented on social engineering countless times because it is truly fascinating and arguably the biggest threat to your organization’s cyber (and physical) security. Business email compromises and supplier impersonation can be extremely hard to detect from the receiving end until losses have been had. My go-to recommendations for preventing these types of attacks involve educating users on common tactics, creating multi-step and multi-person verification processes for payment changes, and, most importantly, fostering an environment in which employees are praised for asking questions like:
- Have I interacted with this contact at our supplier before?
- Have we received a request like this before?
- Are there any indicators of phishing present, such as urgency or fear tactics?
- Are there any misspellings in the email address?
- If I hover over the link, does it look like it leads to my expected destination?
- What resources or personnel can I utilize to verify the legitimacy of this email?
- Should I ask my cybersecurity/IT team to take a look at the email, just in case?
In fact, I’d like to provide some praise to an anonymous company I’ve seen create a very strong cybersecurity culture. Following a BEC/supplier impersonator, they included an email footer in every email alerting contacts to the importance of verifying senders and briefly sharing the indicators of a suspicious request. Here’s an example of what the footer looked like:

This company has become a cybersecurity champion in its industry and regularly reports phishing emails, even more complex ones that make it past their email provider’s filters. Their team strives for and completes 100% of their Security Awareness Training and whistle-blow any suspected phishing emails to their colleagues.
This provides an excellent segue into my top recommendations for building a strong cybersecurity culture.
How to Build a Strong Cybersecurity Culture
- Security Awareness Training – A classic. It sounds obvious, but good security awareness training (cough cough, like the one I curate and deliver to our clients at Edge Networks) is often your best defense in not only bridging the divide in knowledge between different departments and individual employee awareness levels but also in protecting your organization from the most preventable types of attacks.
- Promote a Reporting Culture – We cover this in our onboarding training for all organizations, and for good reason. Regardless of how comfortable someone is with technology and security awareness, it can only do so much good if no one speaks up for fear of being wrong or annoying. From your favorite friendly neighborhood cybersecurity analyst: please bug me! I would much rather take a few minutes to review an email that falsely triggers your Spidey Senses than have multiple users fall for a phishing email due to each of them thinking they’re just paranoid or that it isn’t important since they’ve identified it. I love to spotlight users who report suspected phishing emails or other questionable activity to their executives and leadership teams.
- Lead By Example – If you’re not doing your security awareness training, why should your employees? To foster a strong cybersecurity culture, walking the walk is crucial to creating genuine buy-in for your company. You set the tone that will ripple down through your organization. Pro tip: strike up a conversation with your employees on whether they’ve seen the latest training and tell them what you thought was interesting about it. They just might be one of the first to complete their training next time and either initiate the conversation with you next time or even just take what you said and regurgitate it to their direct coworkers.
- Make Strong Passwords Easy – Invest in a password manager, like 1Password, that gives your employees an easy way to maintain strong passwords. They’ll get a little kick of confidence each time they hear about a password-related compromise, knowing they’re doing their part while potentially even making their lives easier. Enforce MFA to create peace of mind knowing their accounts are extra secure and illuminating illegitimate login attempts. A balance can be found to prevent MFA fatigue.
- Incident Response Plan/Tabletop Exercises – Nothing engages your employees in your cybersecurity culture more than bringing them face-to-face with their roles and responsibilities in the event of an incident. Tabletop exercises, especially, are an extremely effective way to not only test your incident response plan but also build confidence, comfortability, and buy-in regarding your cybersecurity plans and culture.
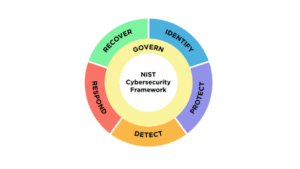
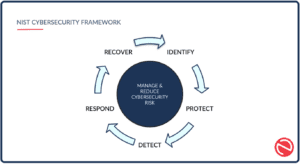
- Align with a Security Compliance Framework – Through compliance assessments, vulnerabilities, areas for improvement, and action items will be identified. We recommend NIST-CSF as a starting point since it’s free, low stakes, and maps well to other compliance frameworks you might want or need to align with in the future. This could look like:
-
- Developers uploading evidence of their secure coding processes or take it as an opportunity to establish them.
- IT team providing data flows and asset inventories.
- The cybersecurity team adding evidence of their detection and monitoring capabilities.
- HR including a copy of the signed employee handbook
- Operations team providing or establishing baseline policies and procedures.
- Executives and business development teams providing the mission statement, supply chain relationships, and identifying state/federal/industry cybersecurity requirements.
A Continuous Commitment to Awareness and Education
The human element of cybersecurity plays a critical role in keeping your organization secure. It’s important to know that a strong cybersecurity culture isn’t just a one-time investment but a continuous, evolving effort. It requires a commitment to education, training, and staying vigilant. When every individual within an organization understands the principles of cybersecurity, it becomes a shared responsibility and a collective shield against potential breaches. By building a culture that values awareness and proactive security measures, we strengthen not only our own defenses but also contribute to a safer digital world for all.