The Rise of Identity Theft
Online transactions offer convenience, but they also come with a dangerous downside: a noticeable increase in cyber threats, especially identity theft. Identity theft has become a common threat that looms over individuals and organizations. Understanding and proactively addressing these threats is crucial for protecting digital and financial well-being.
As we dive into the topic of identity theft, the potential risks involved, and preventative strategies, it’s clear that a comprehensive approach is crucial for security. With this article, we aim to arm individuals and organizations with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate and protect against evolving cyber challenges.
Understanding Identity Theft
Identity theft is a form of cybercrime involving the unauthorized acquisition and use of an individual’s personal information for fraud. The most common forms include:
- Financial identity theft, where criminals use another person’s identity to illegally obtain goods, services, or credit.
- Medical identity theft, which sees perpetrators using someone else’s identity to gain access to medical care or prescription drugs.
- Criminal identity theft, involving criminals impersonating someone else upon being apprehended for a crime.
Additionally, there is the rising threat of synthetic identity theft, where culprits combine real and fake information to create a new identity, complicating the detection and resolution processes.
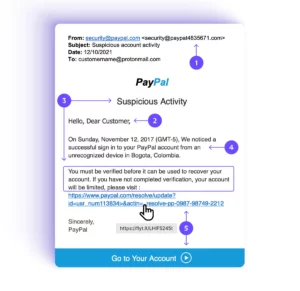
How Identity Theft Works
The methods for identity theft are diverse and increasingly inventive, evolving alongside technology. Phishing attacks are among the most common methods for their prevalence and effectiveness. These attacks involve sending emails that appear to be from reputable sources to trick individuals into revealing personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers. The sophistication of these attacks has grown, making them harder to distinguish from legitimate communications. Attackers often create a sense of urgency or fear, prompting immediate action that inadvertently leads to information being disclosed.
Additionally, hacking has grown more sophisticated, with cybercriminals exploiting security weaknesses to access personal data, often using complex malware and ransomware. Social engineering plays on the human factor, manipulating individuals into willingly sharing sensitive information, targeting what’s often seen as cybersecurity’s most vulnerable spot.
Impact of Identity Theft
For organizations, the repercussions of identity theft can be catastrophic. Beyond the immediate financial losses, they may face operational disruptions, legal liabilities, and a significant erosion of customer trust and loyalty. The long-term reputational damage can deter current and potential customers, impacting the organization’s bottom line and potential prospects. Moreover, the breach of sensitive customer data exposes the organization to regulatory penalties and legal challenges, adding to the complexity and cost of recovery efforts.
Financial institutions, in particular, find themselves targeted more often by identity theft attacks due to the sensitive nature and value of the information they hold. These institutions are often seen as gateways to a wealth of financial assets and personal data for multiple clients. When attackers succeed, the ripple effects are profound as they lead to direct financial losses and a compromise of the integrity of the financial system itself. Clients’ trust, once the foundation of any financial institution’s success, can crumble quickly, leading to a loss of business and a damaged reputation that can take years to rebuild. Additionally, the regulatory repercussions can be severe, with institutions facing heavy fines and increased scrutiny.
The impact of identity theft extends well beyond just financial loss. Individuals may experience significant emotional distress, including anxiety, depression, and a deep sense of violation. The impact on one’s reputation can be just as damaging, with victims sometimes wrongfully linked to crimes committed under their names. Getting back on your feet after identity theft isn’t quick or easy; it often involves a long, complex journey filled with legal steps to take back your identity and repair your financial and social standing.
This wide-ranging impact highlights the urgent need for increased awareness and strong preventive actions. It serves as a clear call to always be vigilant about protecting personal information, especially today, where our digital identities are just as important as our physical ones.
Trends in Cybercrime
The methods employed by cybercriminals evolve with alarming agility and sophistication, complicating the nature of cyber threats and making them tougher to detect. With access to cutting-edge technology, they have what it takes to carry out their attacks, from exploiting vulnerabilities to using machine learning. This ongoing battle between cybersecurity experts and cybercriminals highlights a stark reality: what worked to protect us yesterday might not be enough tomorrow.
Emerging Threats
Among the growing list of emerging cyber threats, deepfake technology and AI-powered phishing scams stand out for their ability to mimic reality with disturbing accuracy.
Deepfake technology uses advanced AI to create incredibly realistic counterfeit videos or audio recordings. This poses a real danger to personal identity and integrity of information, as these realistic forgeries can impersonate individuals, misuse their likeness and voice for fraud, damage reputations, or spread false information.
Similarly, AI-powered phishing scams mark a significant evolution from traditional phishing techniques. Leveraging machine learning, these scams generate highly customized and convincing fake messages or emails, vastly improving their chances of tricking people into revealing personal details.
These threats highlight the increasing capacity of cybercriminals to bypass traditional security measures. It’s a clear call to action for a thorough reassessment and enhancement of our cybersecurity approaches.
The Critical Role of Credit Monitoring
What is Credit Monitoring?
Credit monitoring is a service designed to protect individuals from identity theft and credit fraud. It allows you to continuously oversee one’s credit reports and promptly alerts subscribers to any unusual or unauthorized changes that may signal fraudulent activities. Credit monitoring covers various aspects of one’s credit profile, from new credit inquiries and account openings to alterations in personal information and discrepancies in credit card balances. It serves as an early warning system, empowering individuals to take swift action to prevent potential damage to their financial health and credit standing.
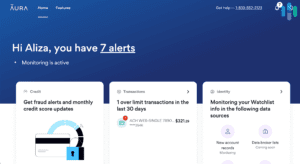
How Credit Monitoring Works
The mechanics of credit monitoring involve an intricate system of checks and alerts that keep subscribers informed of every significant modification in their credit reports. The service works by scanning an individual’s credit report, maintained by major credit reporting agencies, for any new activity or change. This continuous monitoring extends to a variety of transactions and updates, including the opening of new credit accounts, inquiries made by lenders, variations in credit limit, and even minor changes in personal information that could indicate identity theft.
When such a change is detected, the credit monitoring service promptly notifies the individual, usually via email or text message, allowing them to verify the activity. If the activity is unauthorized, the individual can then take immediate steps to address the issue, such as contacting the credit bureau, disputing charges, or freezing their credit, intercepting the efforts of identity thieves and minimizing the risk of financial loss.
At Edge, we recommend services like Aura that provide comprehensive monitoring and insurance for identity theft losses. These tools can be invaluable in providing early warnings of potential fraud.
Proactive Measures in Personal and Organizational Security
Preventive Strategies
Effective prevention strategies use various methods to protect people from the wide range of cyber threats they encounter daily.
- Create strong, unique passwords for different accounts and change them periodically.
- Be cautious when sharing your personal information, particularly on social media and other public forums.
- Employ strong security software that protects against malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks. This software should be kept up to date to counter the latest cyber threats effectively.
Organizational Cybersecurity Measures
For organizations, the stakes are equally high, with the added responsibility of protecting customer and employee data. Enhancing an organization’s cybersecurity posture requires a comprehensive strategy including technological solutions and human-centric approaches.
- Implement policies and technologies such as multi-factor authentication to a critical security layer, making unauthorized access considerably more challenging for cybercriminals.
- Invest in employee security training programs, which are essential in fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness and equipping staff with the knowledge to identify and avoid potential threats.
- Regular security assessments and penetration testing can reveal vulnerabilities within an organization’s IT infrastructure, allowing for timely remediation before these weaknesses can be exploited.
- Data encryption and secure backup practices ensure sensitive information remains protected, even in a breach.
Adopting these proactive measures, both personally and organizationally, constitutes a strong defense against cyber threats like identity theft. By prioritizing cybersecurity, individuals and organizations can significantly mitigate the risk of data breaches, identity theft, and other cybercrimes, protecting their digital and financial well-being in the process.
Best Practices for Individuals
Beyond these foundational strategies, individuals should take these additional steps:
- Regularly review credit reports and financial statements.
- Educating oneself on the latest cyber threats and understanding how to recognize phishing emails and fraudulent websites.
- Use credit monitoring services to keep an eye on any suspicious activity.
Immediate Steps and Long-Term Strategies
In the face of a cybersecurity incident, taking swift and decisive action is crucial to mitigate the impact and to protect your digital identity. Here are some immediate steps to consider:
- Sign Up for Credit Monitoring: Platforms like Aura offer extensive monitoring, alerts for fraudulent activity, and insurance coverage for losses due to identity theft.
- Utilize Banking Alerts: Register for ChexSystems to receive alerts on any attempts to open new bank accounts in your name, especially if your personal identification has been compromised.
- Contact Your Bank: Inform your financial institution of the situation so they can secure your accounts.
- File Reports: It’s essential to file a police report and a complaint with the Internet Crime Complaint Center. Reporting to the IC3 ensures that all relevant government agencies, including the FBI, are aware of the incident.
Beyond these immediate steps, adopting long-term strategies can strengthen your cybersecurity defenses:
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use strong passwords and enable MFA for an added layer of security on all social media and online accounts.
- Trust Your Instincts: If a message or request seems suspicious, it likely is. Verify the authenticity of any unusual requests directly with the sender.
- Collect Evidence: In the event of a hack or scam, gather as much information as possible, such as account handles and phone numbers, to aid in reporting and investigation.
- Raise Awareness: If your accounts are compromised, inform your network to prevent the spread of fraud.
- Verify Support Channels: Always confirm you’re using the correct support contact information by visiting the official website of the service in question.
- Be Wary of Unsolicited Downloads: Legitimate platforms will not request you to download remote desktop software for identity verification.
- Understand Platform Policies: Be skeptical of any requests for money transfers for verification purposes. Legitimate entities usually do not ask for such actions.
- Act Without Delay: Report any suspicious activity to the relevant platforms, your bank, and law enforcement without delay. Additionally, consider signing up for identity theft and credit monitoring services immediately to stay protected.
As Dwight Schrute from The Office says, “Identity theft is not a joke, Jim!”. We highly recommend incorporating these strategies and a vigilant mindset to significantly enhance your resilience against cyber threats.

The Journey To a Secure Future
The battle against identity theft is ongoing, and it demands our persistent attention and action. By staying informed and implementing strong security practices, we can significantly reduce the risk and impact of the threat of identity theft.
For individuals, this means cultivating a culture of vigilance, where regular reviews of credit reports and financial statements become a routine rather than an afterthought. Practices like these are critical in detecting the early signs of unauthorized activity, enabling swift action to avoid potential crises. Beyond personal vigilance, the collective effort of organizations to strengthen their cybersecurity frameworks through advanced policies, cutting-edge technologies, regular security assessments, and comprehensive employee training programs is equally important.
The path forward requires a continuous commitment to learning, adapting, and innovating in the face of new challenges, ensuring that safety and peace of mind remain at the forefront of our efforts to combat cyber threats. Contact us today to get started on your journey to protect your organization from cyber threats.