LockBit 3.0: Navigating a New Frontier in Cyber Threats
When it comes to the latest and greatest cybersecurity threats, one name stands out prominently: LockBit 3.0. In 2022, LockBit was the most active global ransomware group and RaaS provider in terms of the number of victims claimed on their data leak site.
This threat marks a significant evolution in the field of ransomware, characterized by its sophisticated tactics and comprehensive capabilities. LockBit 3.0 has not only exhibited a remarkable ability to adapt to the evolving cybersecurity defenses but has also demonstrated a heightened level of organization and coordination. The group employs advanced encryption algorithms and leverages intricate social engineering techniques, making their attacks particularly challenging to prevent.
In this guide, we dive into the key characteristics and strategies employed by LockBit 3.0, empowering defenders with the knowledge to face this ever-changing and powerful threat. By understanding the nuances of LockBit 3.0’s tactics, defenders can enhance their preparedness, develop proactive defense measures, and contribute to the collective resilience against this threat.
What is LockBit 3.0?
LockBit 3.0 stands at the forefront of modern cyber threats. It represents a highly sophisticated ransomware group that has gained notoriety for its strategic approach and global reach. It has evolved into a major force in the cyber landscape, building upon the tactics of its predecessors to become a dominant player in the world of cybercrime.
LockBit accounted for 27.93% of all known ransomware attacks from July 2022 to June 2023. This number underscores the group’s remarkable efficiency and efficacy in executing cyber attacks, showcasing a level of operational precision that sets it apart in the realm of malicious cyber activities.
What distinguishes LockBit 3.0 from its counterparts is not merely its prevalence but also its methodical evolution. The group continually refines its tactics, incorporating cutting-edge technologies and adapting to the ever-changing cybersecurity landscape. This agility has allowed LockBit 3.0 to outmaneuver traditional defense mechanisms, posing a persistent challenge to organizations of all sizes.
Moreover, the geographical scope of LockBit 3.0’s operations is noteworthy. The group exhibits a truly global reach, with reported incidents spanning across diverse industries and regions. This capacity for international impact underscores the need for a collaborative and globally coordinated response to counter the multifaceted threat posed by LockBit 3.0.
The Evolution of LockBit
The journey of LockBit is marked by a relentless evolution, shaping it into a strong force within the realm of ransomware. Its roots can be traced back to September 2019, when the first signs of activity under the ABCD ransomware banner, the precursor to LockBit, were observed. This early iteration laid the groundwork for what would later become a series of sophisticated and highly impactful cyber threats.
The following timeline is based on information gathered by the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA):
September 2019: First observed activity of ABCD ransomware, the predecessor to LockBit.
January 2020: LockBit-named ransomware first seen on Russian-language based cybercrime forums.
June 2021: Appearance of LockBit version 2 (LockBit 2.0), also known as LockBit Red, including StealBit, a built-in information-stealing tool.
October 2021: Introduction of LockBit Linux-ESXi Locker version 1.0, expanding capabilities to target systems to Linux and VMware ESXi.
March 2022: Emergence of LockBit 3.0, also known as LockBit Black, which shares similarities with BlackMatter and Alphv (also known as BlackCat) ransomware.
September 2022: Non-LockBit affiliates able to use LockBit 3.0 after its builder was leaked.
January 2023: Arrival of LockBit Green incorporating source code from Conti ransomware.
April 2023: LockBit ransomware encryptors targeting macOS seen on VirusTotal
Each phase of LockBit’s evolution introduces new complexities and heightened capabilities. It highlights the group’s commitment to diversifying its tactics and underscores the need for defenders to stay alert to the continuously unfolding saga of LockBit’s evolution.
Key Characteristics of LockBit
What sets LockBit apart are its advanced tactics and extensive capabilities. Here are a few key attributes that define its tactics:
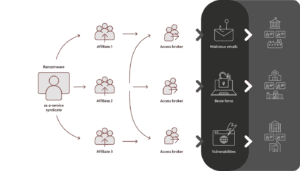
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) Model: At the heart of LockBit 3.0’s operations is its decentralized RaaS model, a strategic approach that leverages a network of affiliates to orchestrate attacks globally. This model not only enhances the group’s scalability but also complicates efforts to trace and attribute attacks, adding an extra layer of complexity for defenders.
Network of Affiliates: LockBit 3.0’s extensive affiliate network, meticulously recruited by the core team, serves as a force multiplier, amplifying the group’s reach across diverse industries and geographical regions. This expansive network contributes to the group’s ability to execute targeted and widespread attacks, presenting a challenge for organizations striving to defend against the multifaceted threat posed by LockBit.
Advanced Tactics: The group distinguishes itself through the application of sophisticated methods such as phishing, exploit kits, and triple-extortion. This demonstrates LockBit 3.0’s prowess in breaching target networks through a combination of technical sophistication and social engineering, underscoring the importance of a multi-faceted defense strategy for organizations aiming to prevent these intricate attack vectors.
Adaptability & Resilience: LockBit 3.0 exhibits remarkable adaptability and resilience in the face of evolving cybersecurity defenses. The group swiftly adjusts its tactics, evades detection mechanisms, and exploits emerging vulnerabilities, ensuring a sustained and impactful presence in the cybersecurity landscape. This ability to pivot in response to countermeasures highlights the dynamic nature of LockBit’s threat profile.
Triple-Extortion Strategy: LockBit 3.0 employs a triple-extortion strategy, integrating data encryption, public exposure threats, and customer/partner coercion. This multifaceted approach intensifies the pressure on targeted organizations to comply with ransom demands, presenting a formidable challenge for those seeking to resist the coercive tactics employed by LockBit.
Decentralized Impact: The decentralized structure of LockBit 3.0 facilitates a global reach, enabling the group to target organizations worldwide. This decentralized impact ensures adaptability and resilience against countermeasures, reinforcing the imperative for organizations to implement proactive defense measures that transcend traditional boundaries.
Understanding these distinctive characteristics is critical for organizations seeking to strengthen their defenses against LockBit’s persistent and sophisticated attacks.
LockBit Tactics & Techniques
LockBit affiliates use sophisticated techniques to exploit system vulnerabilities. From leveraging routine web browsing for silent compromises to exploiting known vulnerabilities and employing social engineering tactics, each method showcases the adaptability and ingenuity of LockBit affiliates. Understanding these tactics is crucial for organizations seeking to strengthen their security measures.
Drive-by Compromise: LockBit affiliates gain access by exploiting vulnerabilities during normal web browsing. Malicious code is executed silently, establishing an initial foothold.
Exploit Public-Facing Application: LockBit affiliates target internet-facing systems, exploiting vulnerabilities like Log4Shell. This allows unauthorized access to victims’ networks.
External Remote Services: LockBit affiliates exploit Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to infiltrate victims’ networks. This direct pathway offers quick access.
Phishing: LockBit affiliates use deceptive emails or messages to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information or executing malicious links or attachments.
Valid Accounts: LockBit affiliates gain initial access by abusing existing account credentials, bypassing the need for technical exploits.
Brute Force Attacks: LockBit affiliates employ brute-force attacks to compromise user credentials for internet-facing RDP and VPN access.
Exploitation of Known Vulnerabilities: LockBit affiliates exploit known software vulnerabilities and security misconfigurations to infiltrate target systems.
Who’s at Risk?
LockBit casts a wide net, strategically targeting organizations across diverse industries worldwide. In the fourth quarter of 2022, the finance, IT, and healthcare industries found themselves among the top three on LockBit’s victim list, indicative of the group’s relentless pursuit of high-value targets.
However, the threat extends far beyond these sectors, as LockBit demonstrates a particular interest in infiltrating critical infrastructure domains.
The following sectors have experienced the impact of LockBit’s sophisticated attacks:
- Financial Services: LockBit’s interest in financial institutions stems from the potential for significant financial gain. The sector’s interconnected networks and vast amounts of sensitive data make it an attractive target for ransomware attacks.
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry is a prime target due to the sensitive nature of patient data and the critical role it plays in public well-being. LockBit’s attacks on healthcare institutions pose not only financial risks but also threaten the continuity of life-saving medical services.
- Food and Agriculture: The agriculture sector, often overlooked in discussions of cyber threats, has become a focal point for LockBit. Disrupting this sector can have far-reaching consequences, affecting the food supply chain and the economies of nations.
- Education: LockBit’s targeting of educational institutions underscores the group’s disregard for the potential societal repercussions of disrupting learning environments. Universities and schools are not only repositories of valuable research but also integral components of community development.
- Energy: Critical infrastructure such as energy grids and utilities are prime targets for LockBit, given the cascading impact an attack on these systems can have on entire regions. The potential disruption to energy supplies poses a significant threat to national security and public welfare.
- Government: Government agencies are frequent targets, with LockBit aiming to exploit vulnerabilities in national and municipal systems. Breaching government networks not only jeopardizes sensitive data but also poses risks to public safety and governance.
- Emergency Services: LockBit’s encroachment into emergency services raises concerns about potential disruptions to crucial response mechanisms. Any hindrance to emergency services can have severe consequences, especially in times of crisis.
- Manufacturing: LockBit’s interest in the manufacturing sector suggests a focus on disrupting supply chains and industrial processes. Targeting manufacturing can lead to widespread economic repercussions, affecting businesses and consumers alike.
- Transportation: Disrupting transportation networks can have cascading effects on the movement of goods and people. LockBit’s incursion into this sector raises concerns about potential disruptions to logistics, posing risks to global trade and infrastructure.
It’s evident that LockBit’s ambitions extend far beyond specific industries. The group’s broad targeting emphasizes a calculated strategy aimed at maximizing disruption and extracting ransom from sectors critical to societal functioning. By examining the varied industries targeted by LockBit, we gain a comprehensive understanding of the extensive reach and adaptability inherent in their tactics.
How to Mitigate LockBit Threats
Understanding the intricacies of LockBit’s tactics is the first step toward building resilience. From implementing essential measures to advanced security protocols, each recommendation is tailored to strengthening your defenses and reducing the likelihood of falling victim to an attack.
- Strengthen Password Policies: Require all accounts with password logins (e.g., service accounts, admin accounts, and domain admin accounts) to comply with NIST standards for developing and managing password policies.
- Sandboxed Browsers: Implementing sandboxed browsers adds a crucial layer of protection, isolating potentially malicious code from the host machine during web browsing.
- Implement Email Gateway Filters: Installing filters at the email gateway screens out emails with known malicious indicators, reducing the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication: Requiring phishing-resistant MFA for critical services adds an extra layer of protection, especially for webmail, VPN, and privileged accounts accessing critical systems.
- Practice Least-Privilege Access: Following the principle of least privilege ensures specific accounts are used for specific tasks, minimizing the potential for unauthorized access.
- Timely Patching & Updates: Regularly updating operating systems, software, and firmware is crucial in preventing exploits, especially for public-facing applications.
- Enhanced Access Controls: Reviewing and auditing user accounts with administrative privileges and configuring access controls according to the principle of least privilege ensures only necessary personnel have access to critical systems.
- Just-In-Time Access Provisioning: Implementing time-based access for accounts at the admin level and higher enhances security by granting privileged access only when needed, automatically disabling admin accounts when not in direct use.
- Network Segmentation: Segmenting networks helps control traffic flows and restrict adversary movement. Isolating web-facing applications further minimizes the potential spread of ransomware.
- Security Awareness Training: Providing practical training on phishing threats and risks associated with email usage, especially in high-volume external communication, is crucial for all employees.
- External Email Warning Banners: Consider adding warning banners for emails sent to or received from outside the organization to alert users to exercise caution.
- Real-Time Antivirus Protection: Installing, regularly updating, and enabling real-time detection for antivirus software on all hosts helps protect against malware threats in real time.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to detect, deter, and ultimately withstand LockBit threats.
The Future of LockBit
It’s clear that LockBit 3.0 has emerged as a threat to organizations in every industry, showcasing remarkable efficiency, global reach, and continuous evolution.
LockBit’s advanced characteristics, including a decentralized Ransomware-as-a-Service model, extensive affiliate network, and triple-extortion strategy, emphasize its sophistication. The group’s broad targeting across industries underscores its calculated strategy for maximum disruption.
Exploring LockBit’s tactics, from silent compromises to exploiting vulnerabilities, provides crucial insights for organizations fortifying their defenses. Looking ahead, understanding these intricacies becomes paramount as LockBit continues to evolve, posing challenges that demand collaborative and globally coordinated responses.
As LockBit charts an unpredictable course in the future of cyber threats, organizations must remain vigilant, continually enhancing their cybersecurity posture to mitigate the multifaceted risks posed by this ever-changing adversary.
Understanding the nuances of LockBit is essential, and our cybersecurity experts are here to help you navigate and implement effective mitigation strategies. From building and strengthening internal security policies to staying up-to-date on emerging threats, our team is dedicated to empowering organizations against the dynamic challenges posed by LockBit and other sophisticated adversaries. Contact us today to get started.